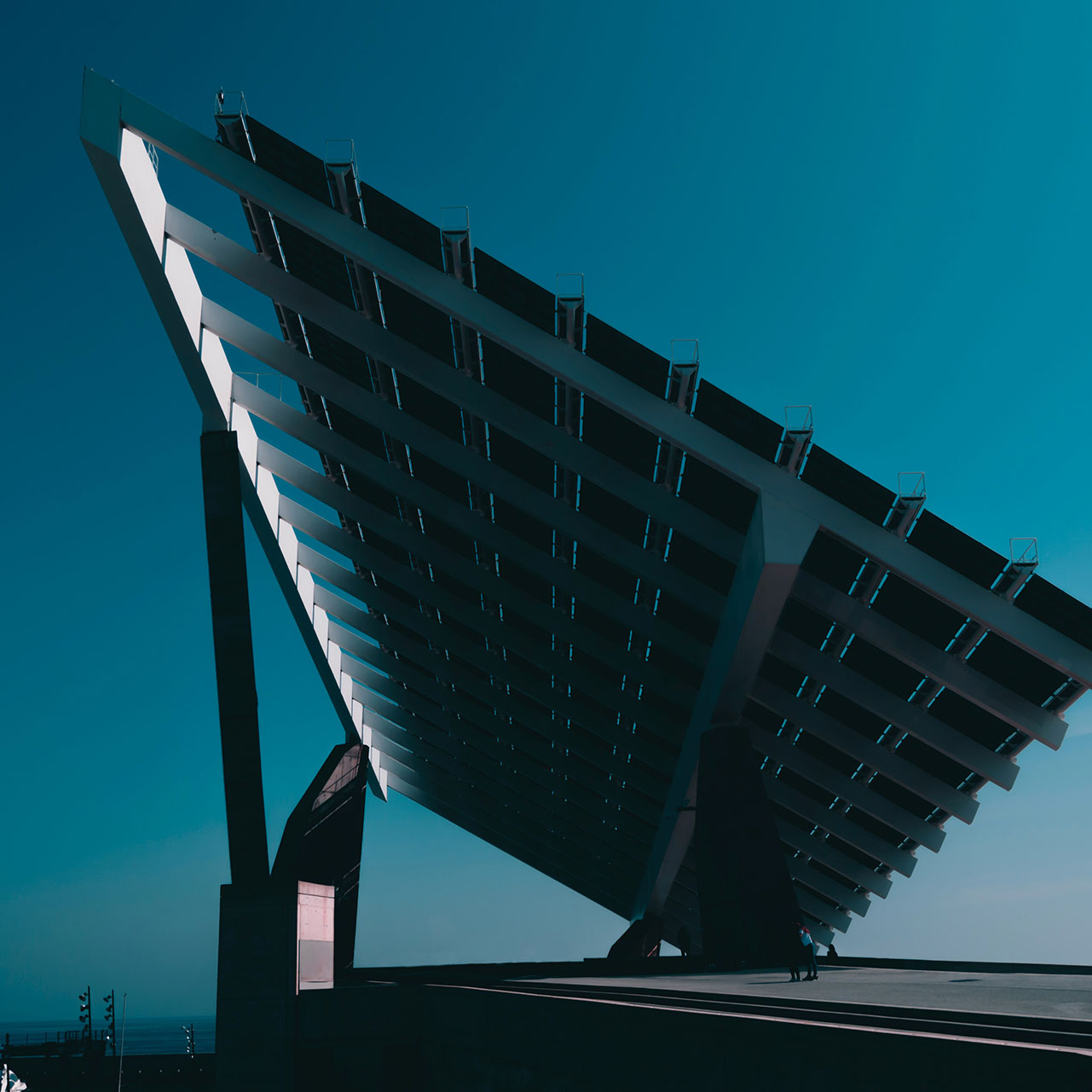
Solar Panels: Solar energy is primarily harnessed using photovoltaic (PV) cells or solar panels. These panels are made of semiconductor materials, such as silicon, that convert sunlight directly into electricity when exposed to sunlight.
Types of Solar Panels: There are two main types of solar panels: monocrystalline and polycrystalline. Monocrystalline panels are more efficient and expensive, while polycrystalline panels are less expensive but slightly less efficient.
Solar Power Systems: Solar panels can be installed on rooftops, in solar farms, or on ground-mounted systems to capture sunlight. The electricity generated by these panels can be used on-site or fed back into the grid.
Solar Inverters: Solar inverters are essential components in solar power systems. They convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used in homes and businesses.
Solar Energy Storage: To overcome the intermittent nature of solar power, energy storage systems like batteries can store excess energy during the day for use at night or during cloudy periods.
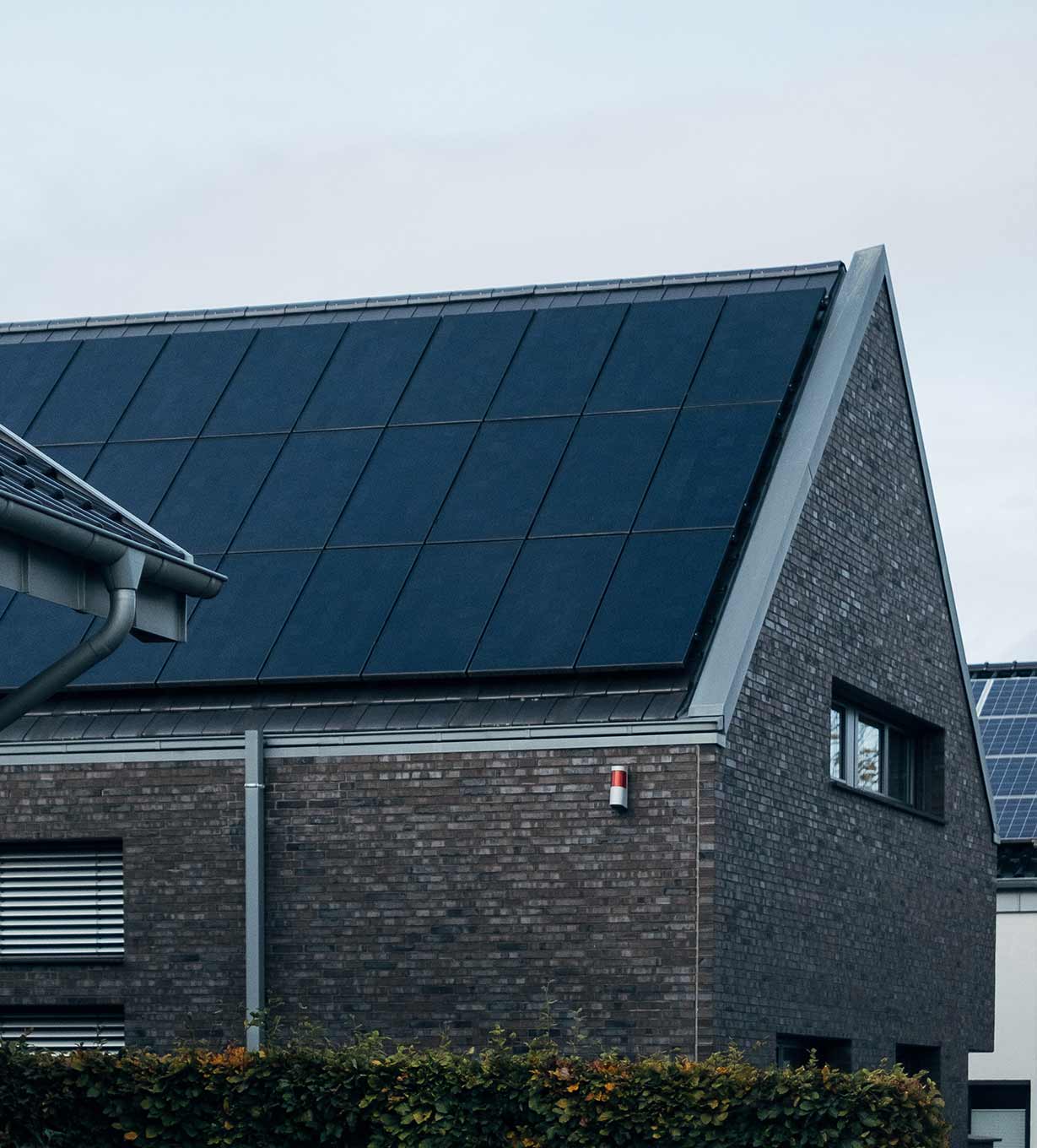
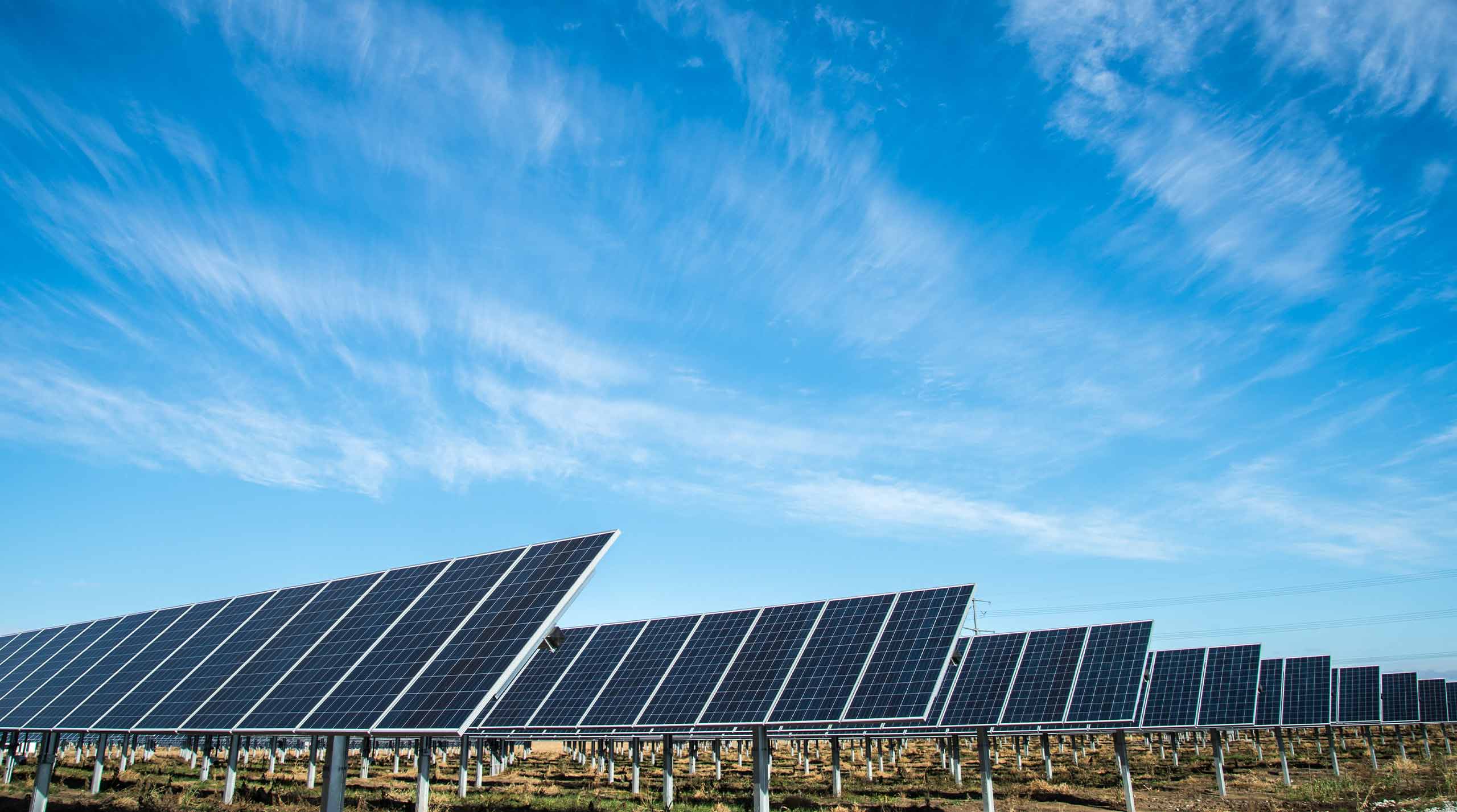


Environmental Benefits: Solar energy is a clean and green energy source that produces no greenhouse gas emissions during electricity generation. It helps reduce air pollution and dependence on fossil fuels.
Economic Benefits: Solar power can provide long-term savings on electricity bills and, in some cases, generate income through government incentives and selling excess electricity to the grid.
Global Growth: The solar industry has experienced rapid growth over the past decade, driven by technological advancements, falling costs, and increased awareness of climate change. Many countries are investing in solar energy as part of their renewable energy portfolios.
Challenges: Solar energy production can be affected by weather conditions, making it less predictable. The manufacturing and disposal of solar panels can also have environmental impacts, although efforts are underway to improve recycling and sustainability.
Future Trends: Advances in solar technology, such as thin-film solar cells, solar tracking systems, and increased energy storage capacity, are expected to further enhance the efficiency and reliability of solar energy systems.
Solar in Space: Solar panels are used extensively in space exploration and satellite technology to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity to power spacecraft and instruments.

Solar energy is a key player in the transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources, and its continued development and adoption are crucial for addressing climate change and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.