How it Works: Wind energy is generated by the kinetic energy of moving air (wind) that is converted into mechanical energy and then into electrical energy. This is typically accomplished using wind turbines, which consist of rotor blades connected to a generator. As the wind blows, it causes the rotor blades to spin, turning the generator and producing electricity.
Types of Wind Turbines: There are two main types of wind turbines:
-
- Horizontal Axis Wind Turbines (HAWT): These are the most common type and have a horizontal rotor shaft. They are often seen in large wind farms.
- Vertical Axis Wind Turbines (VAWT): These have a vertical rotor shaft and are less common. They can capture wind from any direction and are suitable for urban or smaller-scale installations.
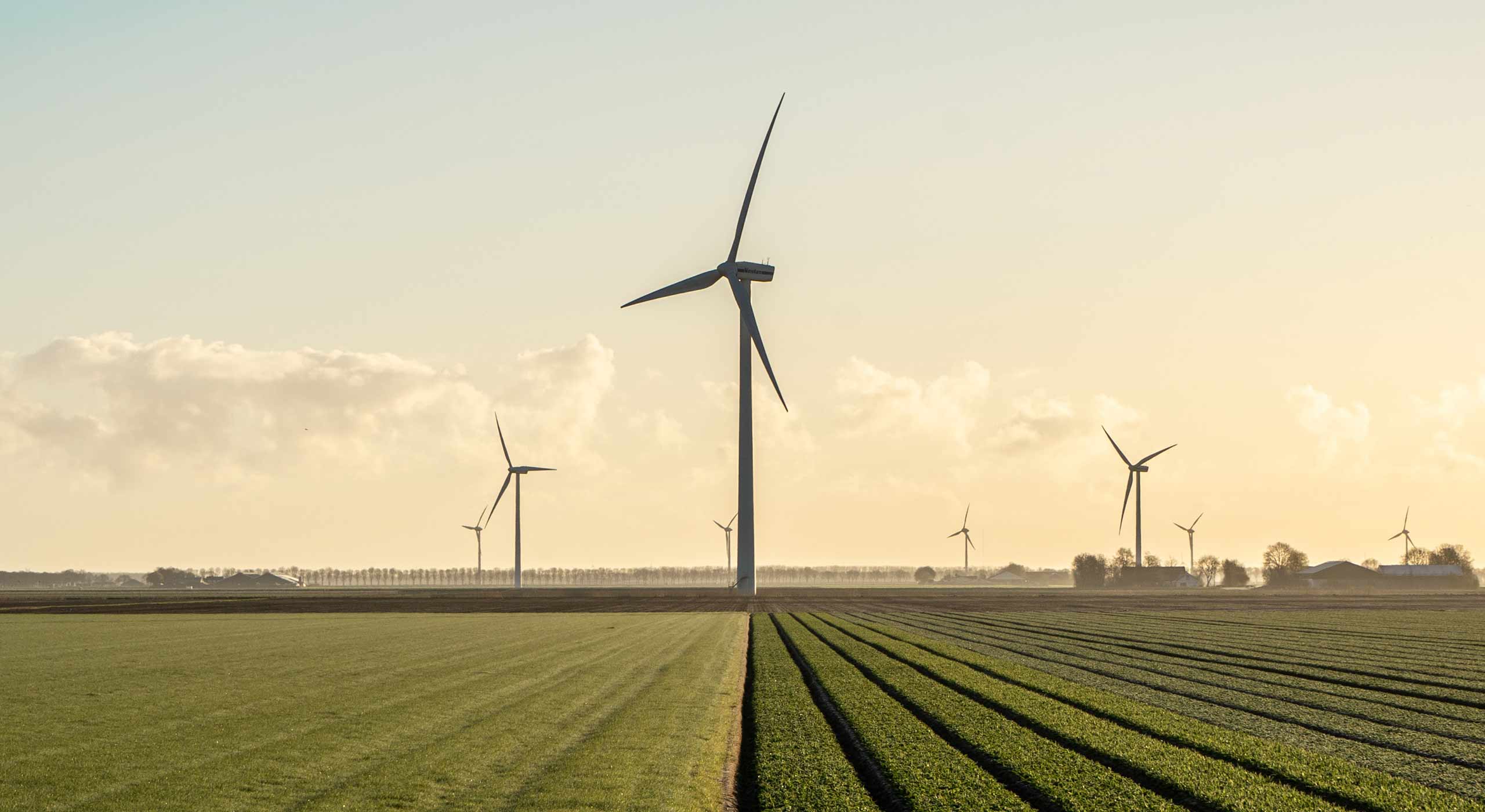
Wind Farms: Wind turbines are typically grouped together in wind farms, which can range in size from a few turbines to hundreds. Wind farms are strategically located in areas with consistent and strong wind patterns, such as coastal regions, plains, or mountain passes.
Advantages:
-
- Clean and Sustainable: Wind energy produces no air pollution or greenhouse gas emissions, making it an environmentally friendly energy source.
- Renewable: Wind is a renewable resource, and as long as the wind blows, energy can be generated.
- Reduced Energy Costs: Wind energy can help reduce electricity bills for consumers and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.


Challenges:
-
- Intermittency: Wind is not constant, and its availability varies, leading to intermittent energy production. This challenge can be addressed with energy storage solutions and a diverse energy mix.
- Visual and Noise Impact: Some people find wind turbines visually unappealing, and they can produce noise, although modern designs have mitigated these issues.
- Space Requirements: Large-scale wind farms require significant land or sea space, which can impact ecosystems and communities.
Capacity Factors: The capacity factor of a wind turbine or wind farm measures how much electricity it generates compared to its maximum potential. Onshore wind farms typically have capacity factors ranging from 25% to 45%, while offshore wind farms often have higher capacity factors due to more consistent winds.
Global Growth: Wind energy has experienced significant growth worldwide in recent years. Many countries have invested in wind power as a key component of their renewable energy strategies.


Offshore Wind: Offshore wind farms, located in bodies of water like oceans and seas, are becoming increasingly popular due to the potential for higher and more consistent wind speeds. They can also be located closer to population centers, reducing transmission losses.
Technological Advances: Ongoing research and development have led to more efficient and cost-effective wind turbine designs, including larger turbines with taller towers and improved materials.
Environmental Impact: While wind energy is generally considered environmentally friendly, its impact on local ecosystems, bird migration patterns, and marine life should be carefully considered and mitigated during planning and construction.
Wind energy is an important component of the global effort to transition to cleaner and more sustainable sources of electricity generation, contributing to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the effects of climate change.